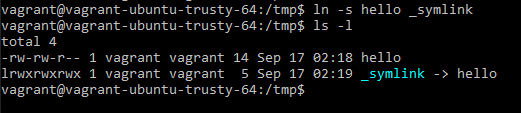
Image 1. The compilation process
When we try to compile a file (e.g. main.c), we need to understand what the system does. The figure above explains the process of compiling these files.
- We need to use a compiler (e.g. gcc)
- The command to compile with gcc is: gcc filename.c
- The output is the executable file a.out (See image 2)
Image 2. Compilation example